NMN vs NR: What's the Difference?
What is NMN?
NMN stands for nicotinamide mononucleotide, a molecule naturally occurring in all life forms. NMN is the direct precursor of the essential molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and is considered a key component to increase NAD+ levels in cells.
What is NR?
Of all the NAD+ boosters - compounds which either convert directly into, or contribute in some way to the process of creating NAD+, nicotinamide riboside (NR) has been the most extensively studied - mostly in animals.
In rodent studies NR has been shown to have a variety of different effects desirable for different people looking for different things. In one study, mice who were fed a diet high in both sugar and fat in order to quickly create obesity, gained less body fat and demonstrated increased insulin sensitivity when taking an orally-administered dose of NR.
Mice receiving the same size dose of NR as the obesity study (400mg per kilo of bodyweight) were also found in another study to have reversed mitochondrial damage and increased mitochondrial biogenesis, the process through which mitochondria are created.
Finally, neurological benefits from NR supplementation were also confirmed in rodents, including neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and reduced beta-amyloid build up in the brain, a strong indicator of Alzheimer’s risk.
“Whether taking nicotinamide riboside will have the same effects on delaying aging or improving mitochondrial function in humans as it does in animals is unknown,”writes famed longevity expert Dr. Rhonda Patrick on her blog.
“However, when people with type 2 diabetes took a nicotinic acid derivative (an NAD+ precursor), they exhibited improvements in mitochondrial function in their skeletal muscle as well as increased NAD+ levels in their muscles”.
NR vs NMN Molecule
There are multiple precursors to NAD+, each with its own physiologic effects. Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a popular one with several notable benefits over other precursors like niacin (NA) and niacinamide (NAM). NA, for instance, may induce uncomfortable flushing, while NAM may inhibit sirtuin at high doses, both undesirable effects.
“Therefore, administration of niacin or niacinamide is unlikely to be widely adopted for maintaining health and function with aging,” researchers wrote in Nature Communications.
Within your body, nicotinamide riboside is converted into NAD+, a helper molecule that exists inside each of your cells and supports many aspects of healthy aging.
Like other forms of vitamin B3, nicotinamide riboside is converted by your body into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme or helper molecule.
Nicotinamide riboside supplements — such as niagen — have quickly become popular because they appear to be especially effective at raising NAD+ levels (Trusted Source). Nicotinamide riboside is also found in trace amounts in cows’ milk, yeast and beer (Trusted Source).
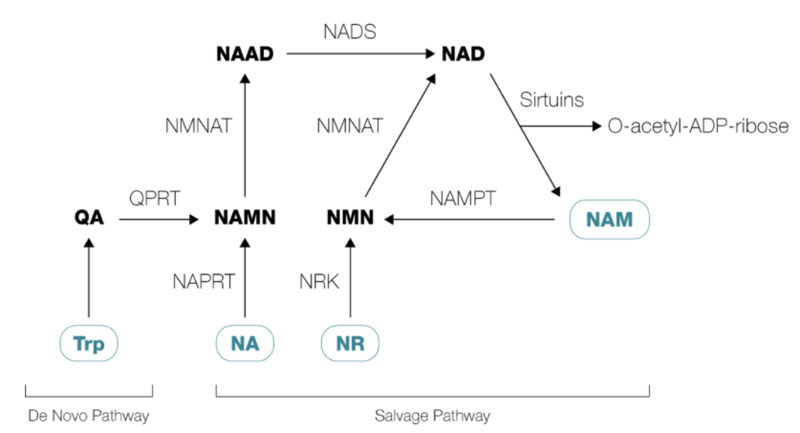
Most of the NAD+ precursor research is done with NR. However, as you can see from the image above, NMN converts to NAD+ whereas NR must first be converted into NMN before it can be converted into NAD+, so it makes more sense to use NMN for NAD+ augmentation.
The image above also shows how niacin (NA) also finds its way to become NAD+. Niacin is also a useful supplement to use in increasing NAD+ levels. You just need to limit the dose to about 25 mg, which most is a dose low enough not to cause any flushing. Higher doses are not likely as effective as NMN and exercise in producing NAD+.
NMN vs NR: Dr Sinclair
There has been few, if any, head to head research published comparing Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR).However, Dr. Sinclair recently said he takes NMN instead of NR based on research he did that found NR did not work at all, while NMN increased the endurance in older mice such that they were able to run twice as far as those on placebo.
NMN has much stronger record of benefit to humans in clinical studies
- NMN has much stronger record of benefit to humans in clinical studies
- NMN treatment increased muscle insulin sensitivity
- NR did not improve insulin sensitivity in trials
Bioavailability Issues with NR and NMN
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) both have very poor bioavailability and if not improved, a tiny fraction is able to make it to the bloodstream and reach tissues throughout the body.Delivery methods that improve the bioavailability are far more important than which molecule is used.
Now, both NMN and NR are available in Liposomes, which protect them from digestion even more than sublingual delivery. Liposomes release the payload in the bloodstream slowly over 24 hours, greatly minimizing the surge in NAM that is known to cause problems with standard NMN and NR capsules.


Comments
Post a Comment